Mycotoxins, their pharmaceutical and military use and how they affect buildings and occupants

What are Mycotoxins?

Mycotoxins are chemicals and semi volatile, their main human exposure route in a building related illness is inhalation, ingestion although dermal exposure may be an issue in extreme situations. Chemical mycotoxins will be on the surface or within spores and dust and fragments. The particles of greatest concern are less than 8 micron where this size by passes all human defences to increase toxicity dose. The dose increase occurs as the smaller fragments carrying inflammagens enter the blood stream through the lungs. Note the term inflammagen and NOT mycotoxin.
This size is often associated with hyphal fragments which are from dead spores and hyphae. As mould dies or dries our it desiccates and fragments. These fragments enter the lower respiratory system where the mycotoxins/inflammagen can be absorbed directly into the blood stream . This inoculation increases exposure by 40 times over normal exposure and whole spores. These inflammatory contaminates can be identified and removed or reduced. A company that can assist in reducing exposure is www.buildingforensics.co.uk who specialise in environmental assessments and risk reduction. Note as professional Indoor Environmental Hygienists , we do not see mycotoxins as the main source of Building Related Illness.
Military WMDs
Military WMDs
Pharmaceutical industry
Pharmaceutical industry
Home Mycotoxin
Home Mycotoxin
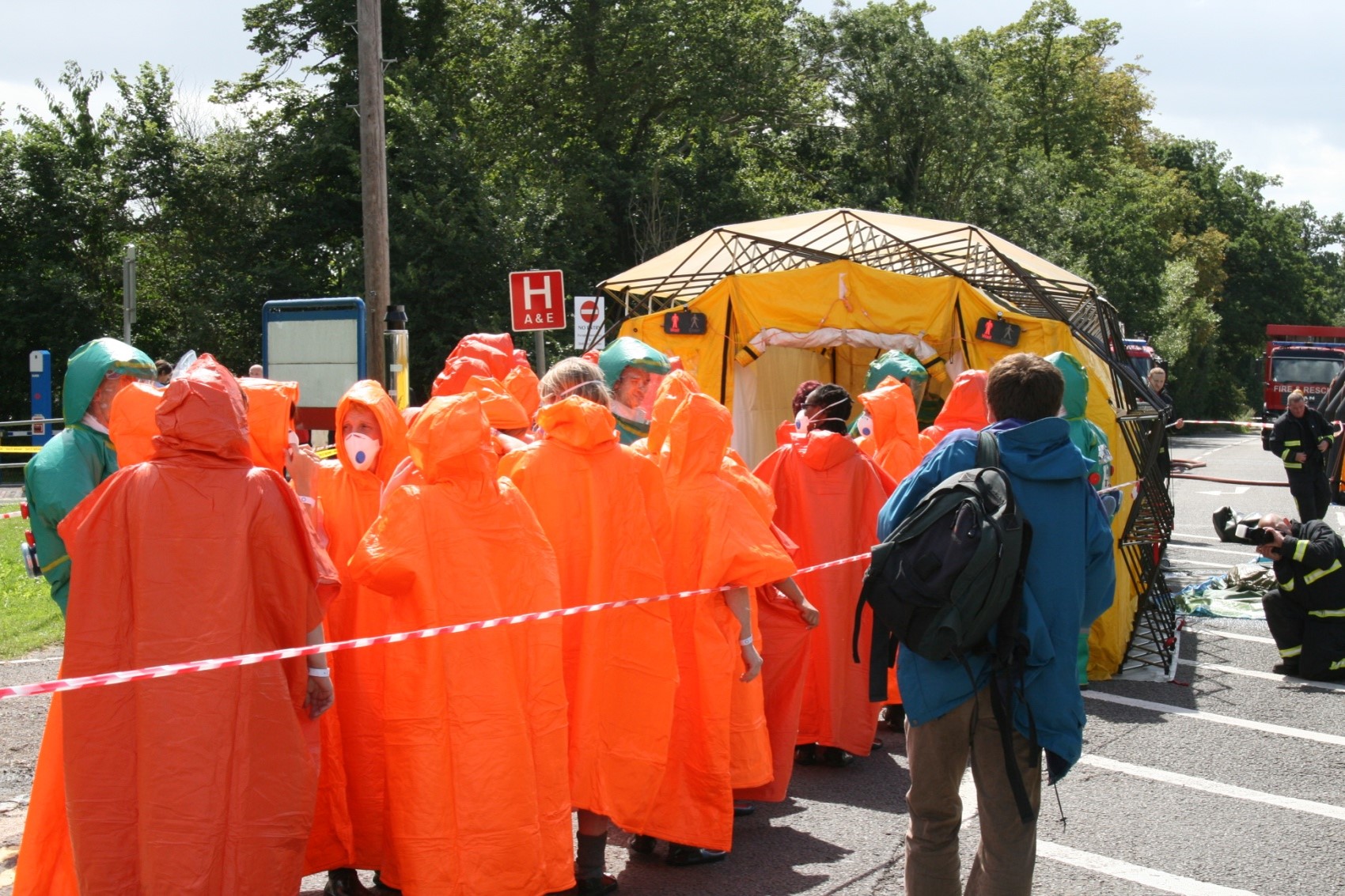
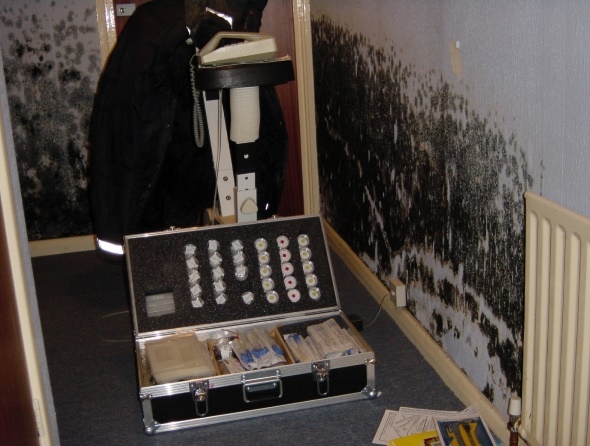
Mycotoxin WMDs

Emergency Services and NHS training for typical Mycotoxin /CBR event. Picture courtesy Jeff Charlton of Building Forensics umpire/observer at the event.

Mycotoxins have been developed as Weapons of Mass Destruction (WMDs) and used by USA in Laos, known as yellow rain. Sadam Husein reportedly used them against the Kurds and believed to have use them in the Iraq war. The same mycotoxins used in WMDs often and usually develop in water damaged homes and can be a major contributor to building related illness. Most medical professionals only accept ingestion as a route to poisoning but the military rely on skin penetration and respiratory exposure for weaponisation.
Pharmaceutical industry

The pharmaceutical industry has utilised the power of mycotoxins since the initial discovery of the mycotoxin from Penicillium by Alexander Fleming. Today mycotoxins are used as anti-rejection drugs in transplant surgery, which in regulated dose have the ability to turn off the immune response system. Unfortunately, these same mycotoxins when present in a home will turn off or affect the immune system and many serious symptoms can be expected to develop.
This photo shows a typical client bedside or kitchen table. A variety of binders, antifungals, and Glutathione. None likely to work effectively while they remain exposed to mycotoxins and other human pathogens. Biological loading must be reduced for treatment to be effective
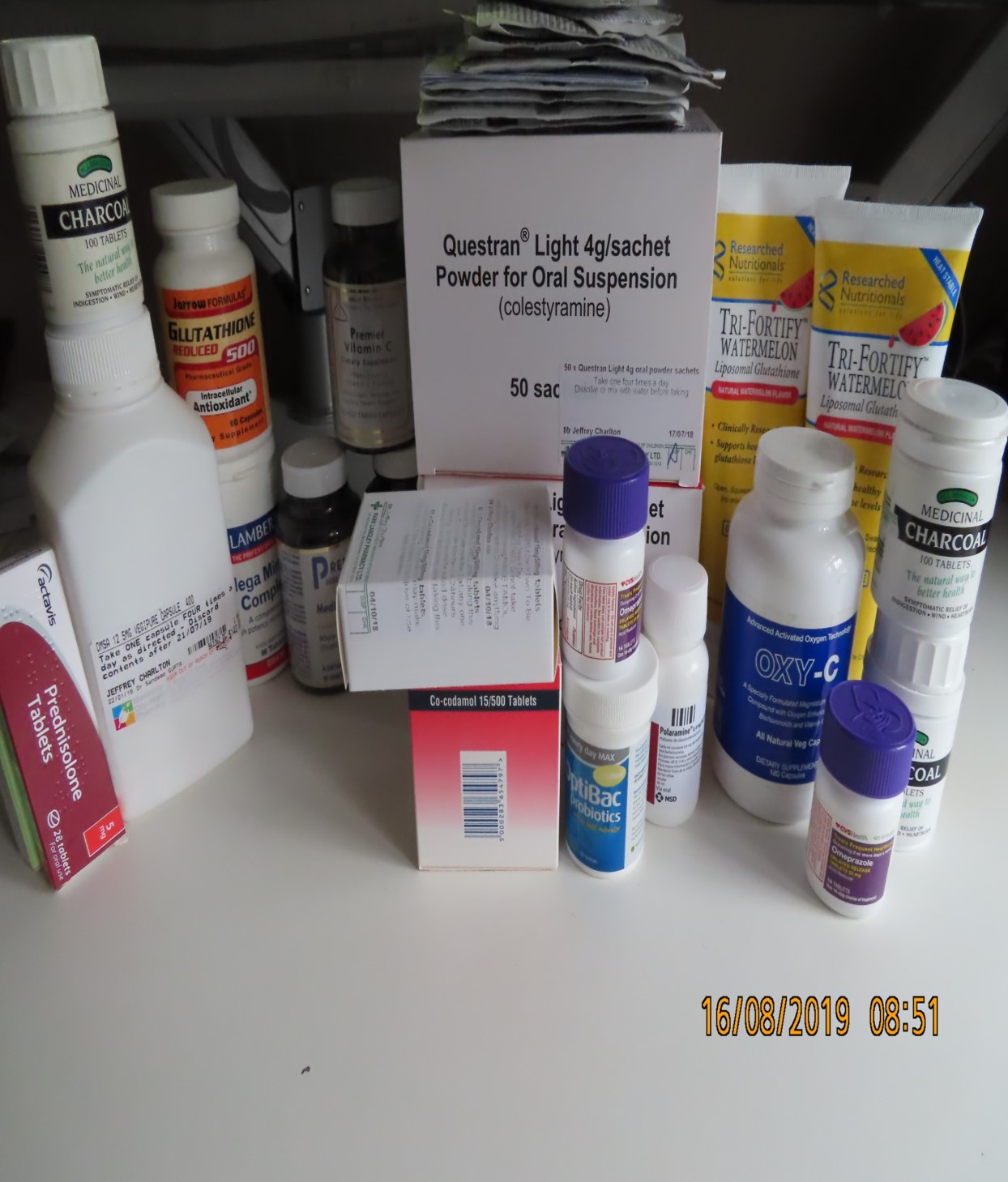
Mycotoxins in the Home
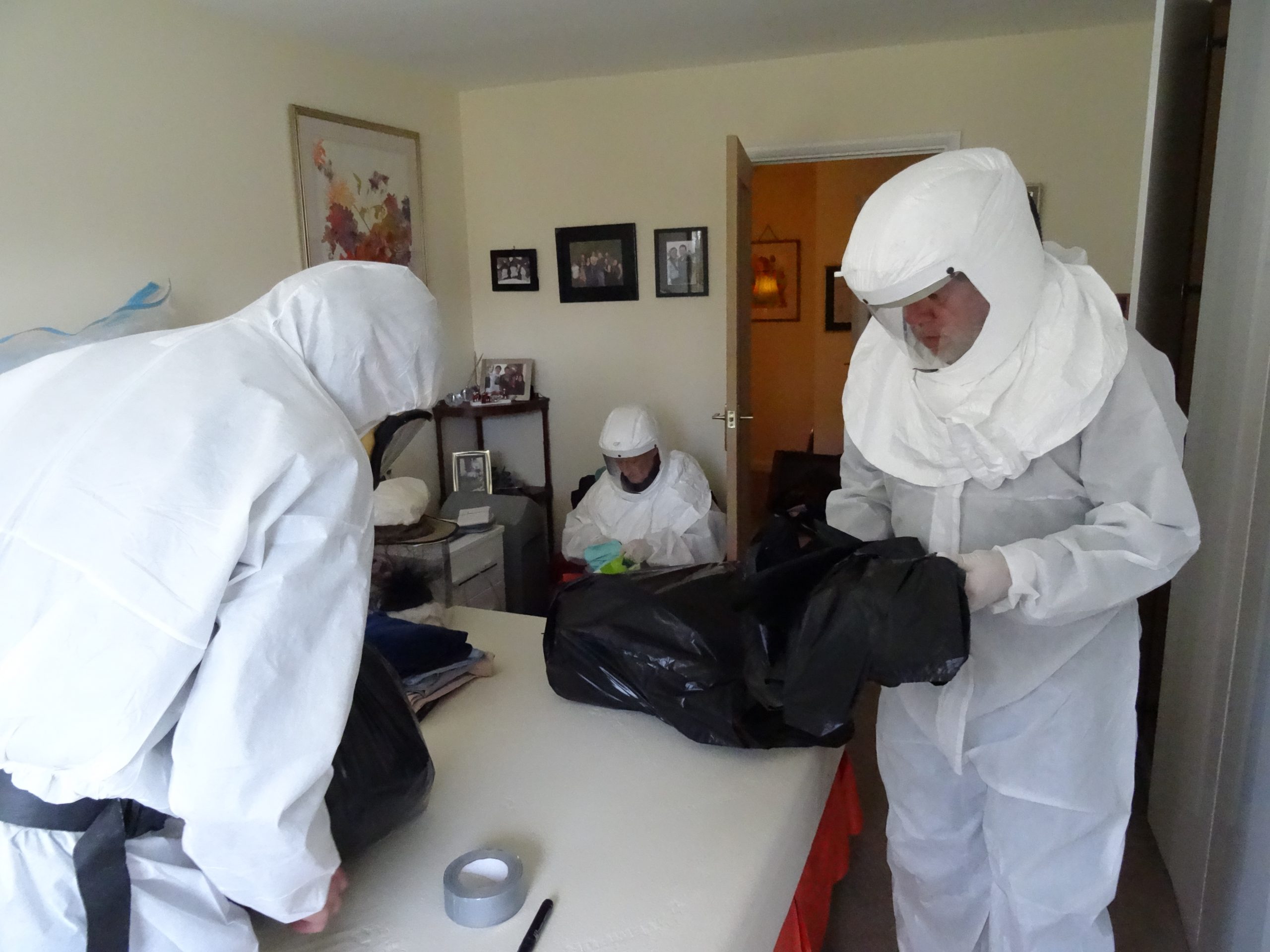


These clients are in their 80s. I had to equip and train and help them take treasured belongings from their home affected by Mycotoxins
Many moulds are said to be toxic but only become toxigenic when they produce harmful mycotoxins. Building occupants suffering mycotoxicosis are often unaware of causation and relate their symptoms to bacteria, mould, virus or just illness. Mycotoxins are extremely stable chemicals and cannot be killed. They do not disappear and when present will remain active for years unless removed. Treatment is often using “Binders” but again continuously inhaling or being having skin exposure will simply see any treatment fail. Mycotoxin exposure must be removed to allow any form of treatment to work. While mycotoxicosis is a recognised mould illness, only a recognised medical professional should consider mycotoxin testing as there are other triggers likely to be as or indeed more likely to be causation.
While many undertake urine tests for mycotoxins, the ones analysed are found in food and were developed by government agencies for food safety. It should be remembered the handful of mycotoxins routinely analysed in urine samples are dwarfed by the hundreds of thousands of different moulds and bacteria capable of working in synergy to affect human health. Absence of evidence is not evidence of absence.
See mycotoxins which are routinely found in people homes suffering building related illness, and immune response issue. They usually develop following some form of water damage and are found in brand new homes and old buildings.

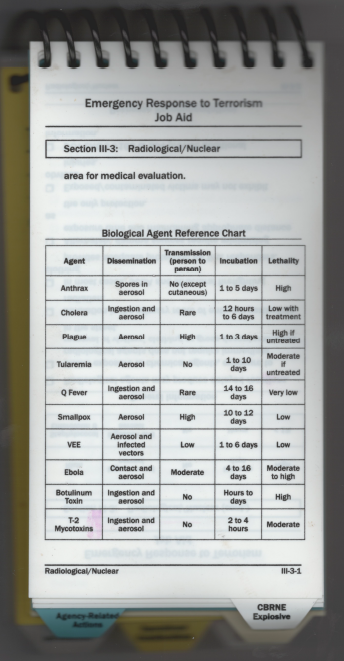
This handbook was issued to Jeff Charlton during Hazmat Homeland training in USA. Note the T2 myctoxin same lethality as EBOLA.
The small amount of mould shown under bathroom carpet was producing T2 toxin. This was my 28 year old daughters brand new home and within 4 months of moving in was diagnosed with final stages of Leukaemia. Her GP sent her to hospital, University College Hospital in London who after blood tests phoned to say they were sending an ambulance to start immediate Chemo and radiotherapy as she had no immune system. Luckily, I intervened and refused the treatment and even more luckily she agreed. Georgie made a full recovery within 6 weeks after exposure ceased. This may be seen by some as scare mongering, but these issues are recorded on NHS files.
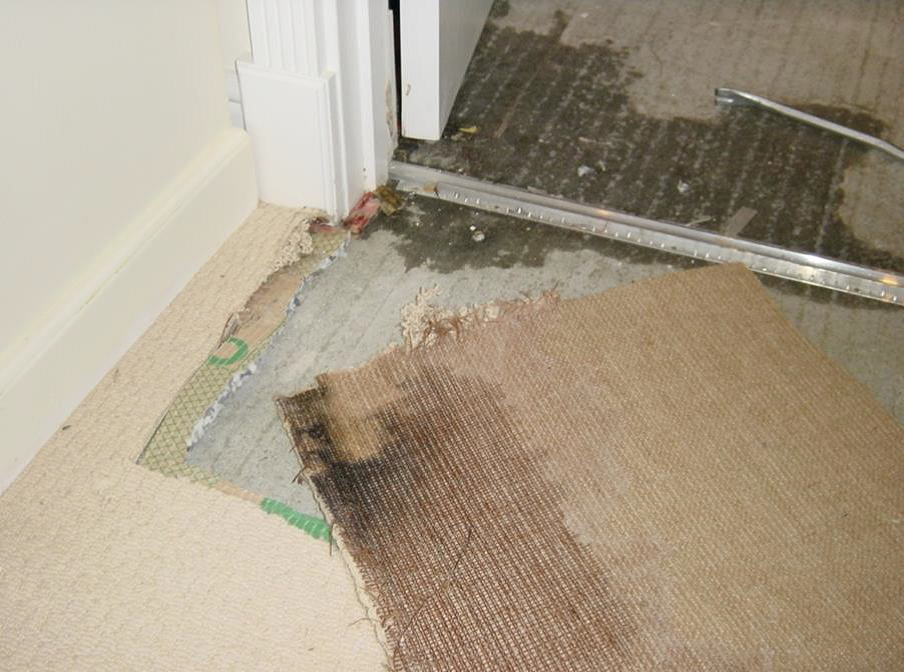

T2 Toxin developing in many homes of sick people we investigate. This example was in my daughters brand new house and resulted in her being admitted to University College Hospital London. Treatment for advanced Leukaemia with chemo and radiotherapy was about to start. Her remarkable recovery astonished doctors when she refused treatment after 6 weeks staying away form home and all symptoms disappearing.

This unusual photo shows Stachybotrys covering all walls in a local authority ground floor apartment. The occupants were extremely healthy , no health impact and as the Stachy was in full control it didn’t need to produce defence mycotoxins. Even mould feared to be toxic are not necessarily producing toxins.
While mycotoxicosis is a recognised mould illness, only a recognised medical professional should consider mycotoxin testing as there are other triggers likely to be as or indeed more likely to be causation.
Inline Support 24/7
We will assist you with your inquiries
Best Quality
Greate choice for your beautiful house
Secured Payment
All your payment information is safe
Money Back Guarantee
Free 100% refund for 30 days
Free Shipping
Free shipping on all order over $88.00
Want something or need advice?
WE CAN HELP WITH YOUR PLANS

CATALOGUE
2019
- Get it Free
- View Online
STORE
APPOINTMENT
Our advisors can
help you with your
layout and decor project
The production and reabsorption of mycotoxins

Please remember building related illness and the above symptoms can be caused by a variety of other issues from inflammagens , bacteria to VOCs. Mycotoxins may be only one trigger. Neurological conditions such autism, Alzheimer’s disease, multiple sclerosis, and Parkinson’s disease. Diseases and symptoms linked to mycotoxin exposure include fever, pneumonia-like symptoms, heart disease, rheumatic disease, asthma, sinusitis, nose bleeding, cancer, memory loss, vision loss, chronic fatigue, skin rashes, depression, ADHD, anxiety, and liver damage. A study of patients with chronic fatigue found that all the patients had high levels of mycotoxins in the urine. (Ref Regenerus)
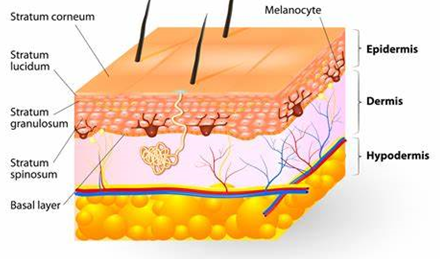
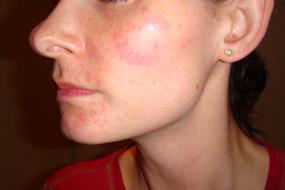
Mycotoxins & skin contact
When a medical professional confirms mycotoxins may be affecting health there is of course a requirement to reduce exposure. Total elimination in everyday life may be impossible but reducing levels to below the trigger or tipping point may be achieved. Some people react to clothes and close skin contact such as soft furnishings and bedding.
The skin is the bodies largest organ. Whatever is absorbed through the skin bypasses the liver and is absorbed directly into the bloodstream without being broken down. This may mean even small amounts of mycotoxins can have increased potency through the skin and may have negative health effects within 60 seconds.
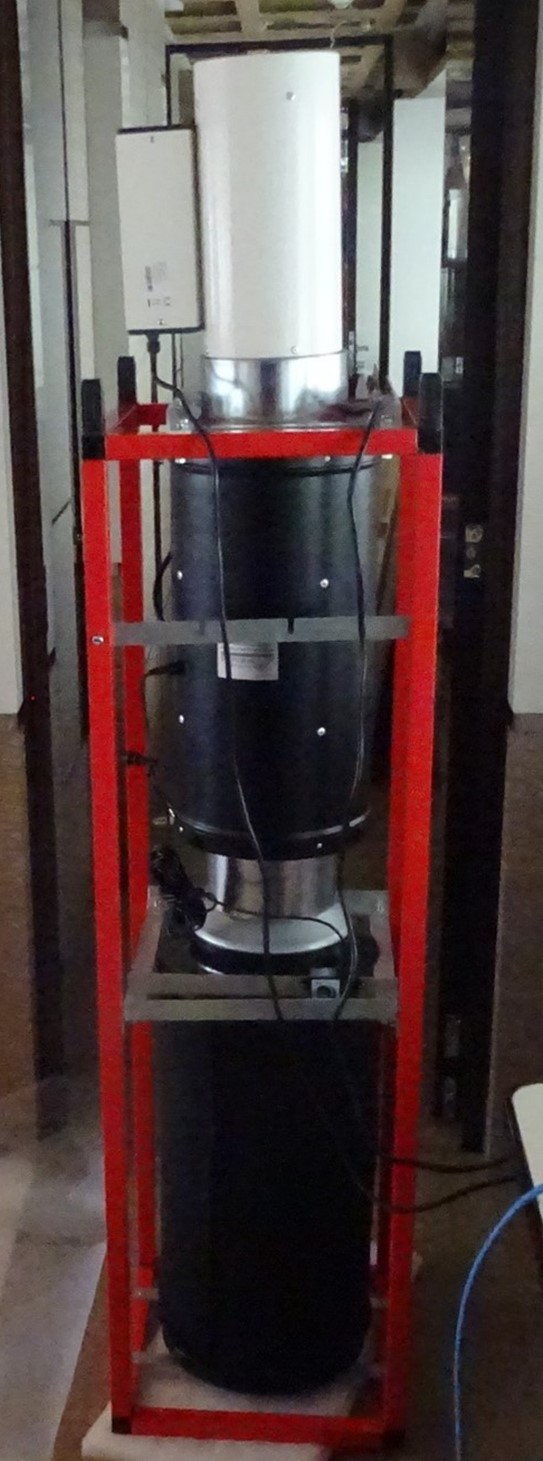

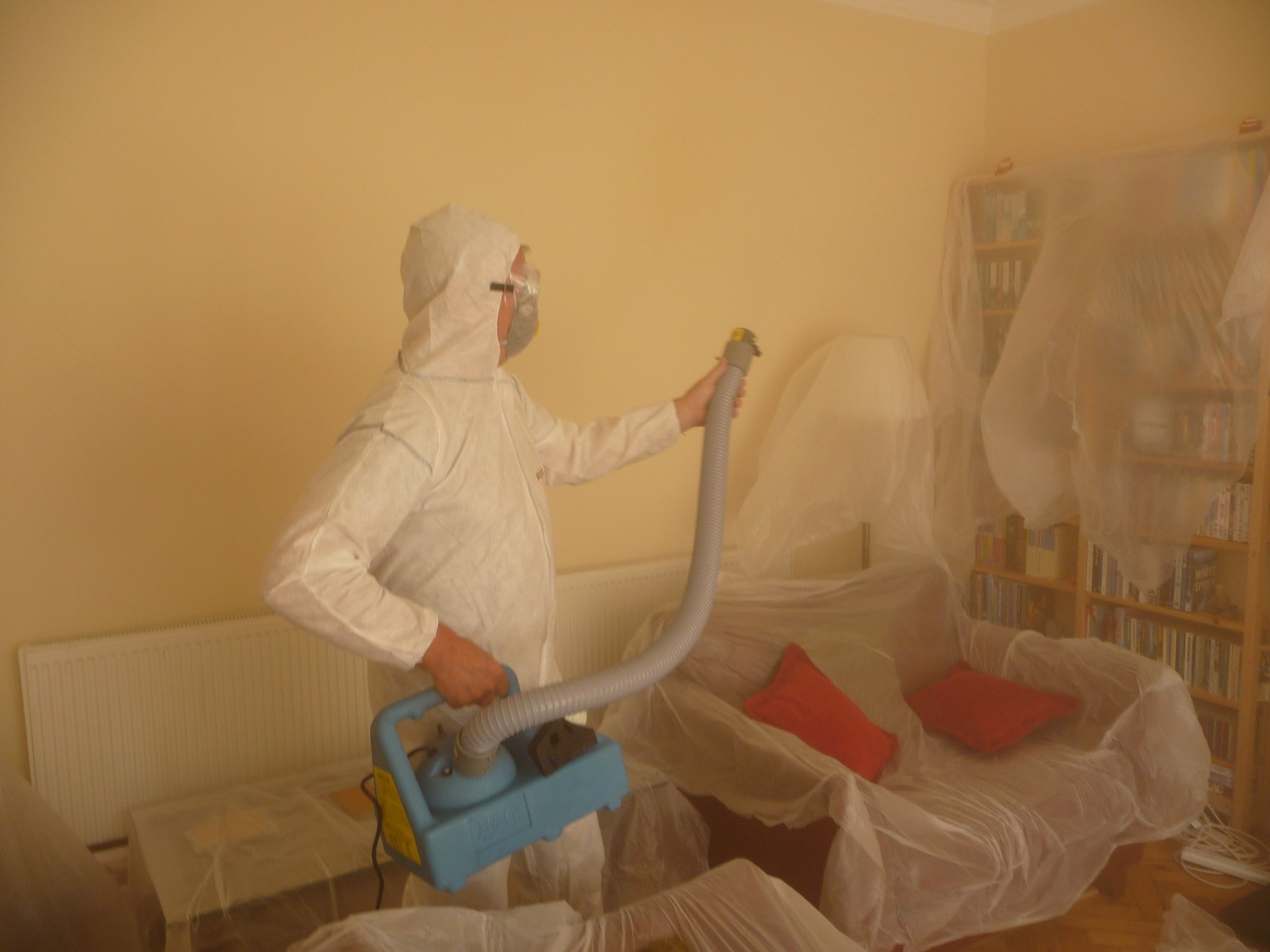
This machine is part of a process where we create an environment which removes or reduces mycotoxins. The protocol currently under patent pending, involves building a mobile enclosure where items are placed into an atmosphere which encourages mycotoxin release and removal.
This manufactured environment takes temperatures to a point where the semi volatile mycotoxins migrate where they and their carriers are both absorbed and removed and or oxidised.
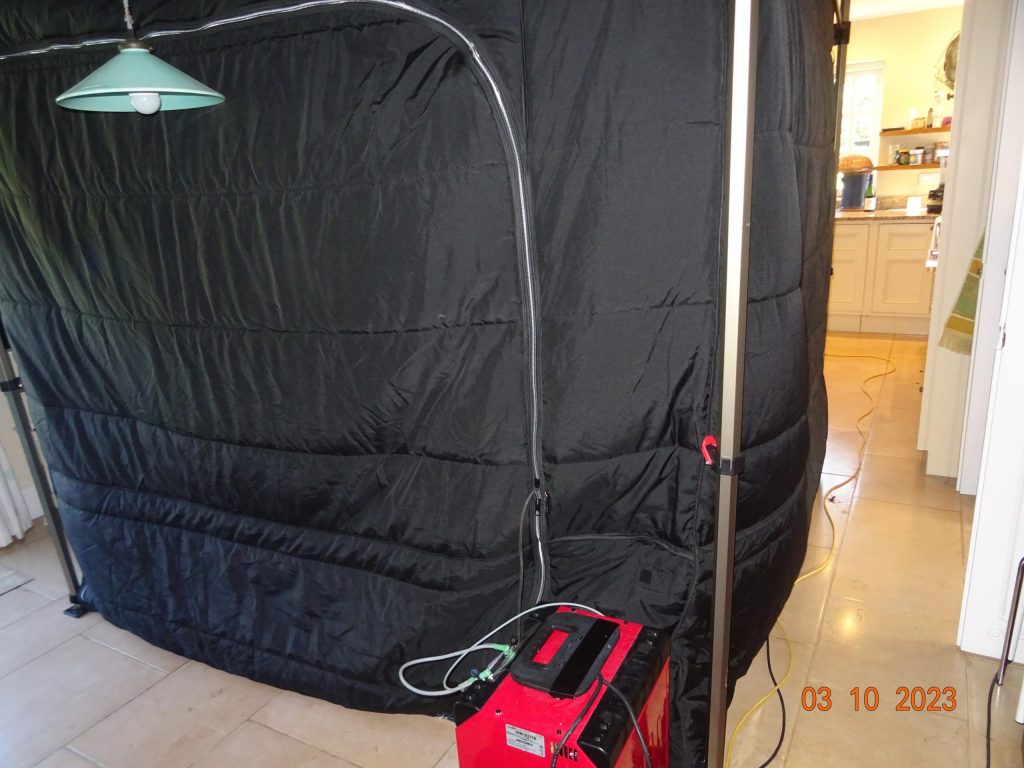
The process lasts on average 4 hours and requires 2x 240 volt supply sockets and a floor space of 10 x 10 feet
Mobile Environmental Enclosure 10 x 10 feet x 8-10 ft high
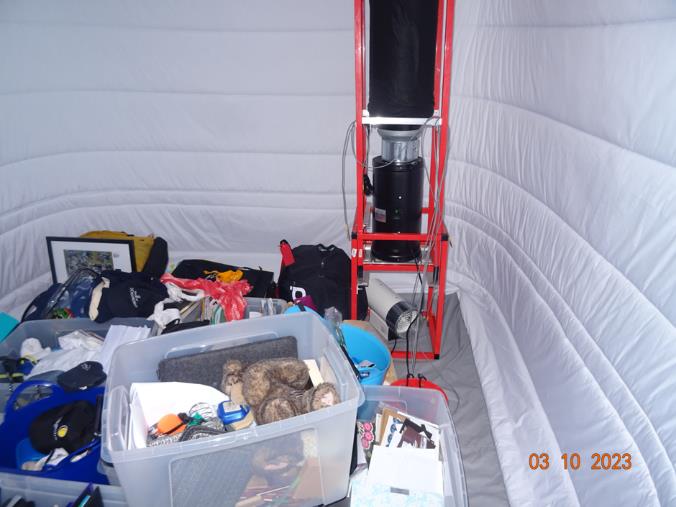

Clothes racks

Mycotoxin in the air
Although mycotoxins are semi volatile they due not move into the air on their own under normal circumstances. However, they are carried into the air by hyphal fragments which are part of the toxigenic species. These fragments have surface contamination. As previously mentioned, Hyphal fragments are known to be in the high risk and hazard to humans as they can bypass human defences. This means hyphal fragments can enter the lower respiratory system where similar to dermal contact , can be absorbed directly into the blood stream.
These hyphal fragments will of course carry inflammagens, mycotoxins and bacteria.
As there isn’t a chemical or any form of decontamination process to neutralise these pathogens, removal is the only solution. Many companies promote decontamination, but you will not find any verifiable sustained evidence, relying only on sales patter.
have patented air scrub which removed airborne contamination at all levels and conquers the usual issues of stratification. www.buildingforensics.co.uk and www.airscrub.co.uk
Verification in a medical facility
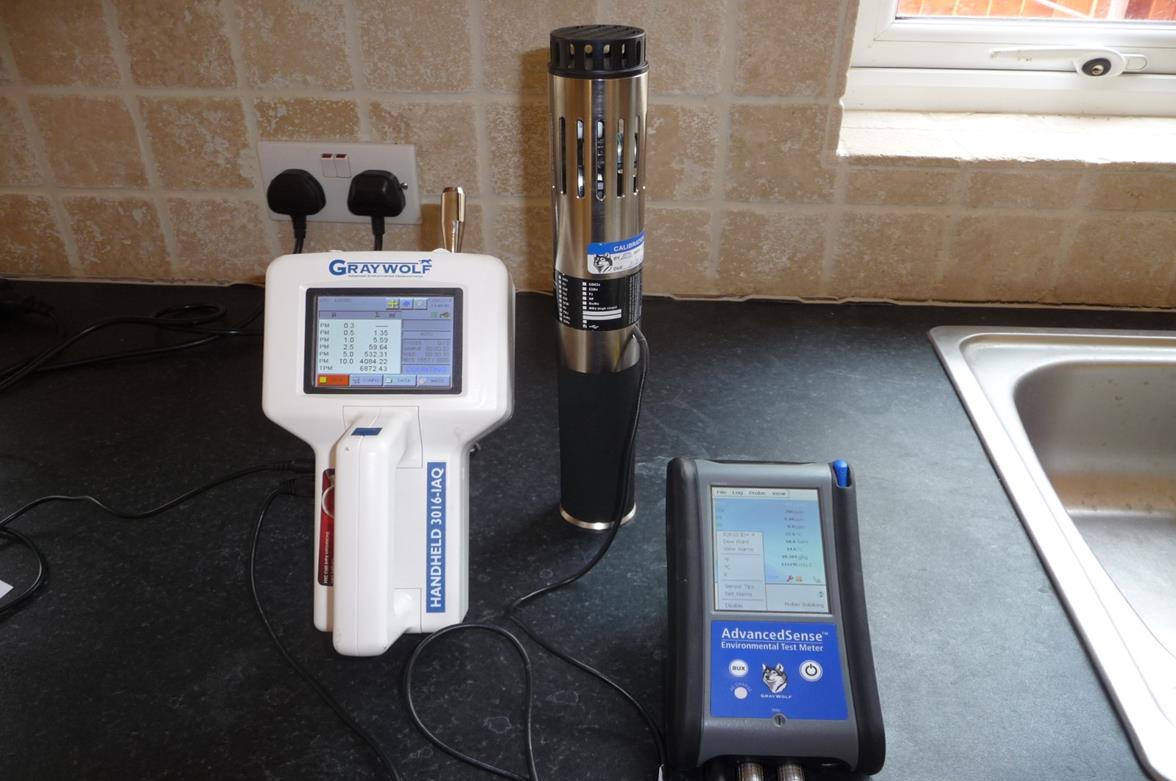
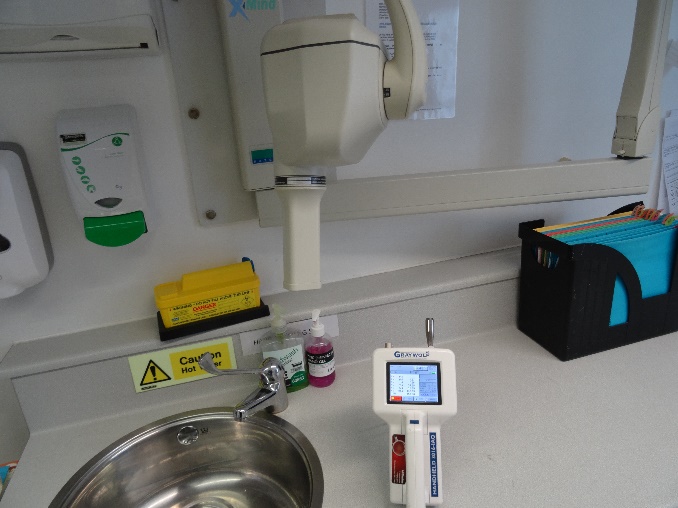




Using the only fine particle cleaning protocol used for CIRS,general inflammatory response.

Using several of these it took months to arrive at the levels of air cleaning and even then stratification issues showed contamination levels increased after the machine was removed.
Mycotoxin on surfaces
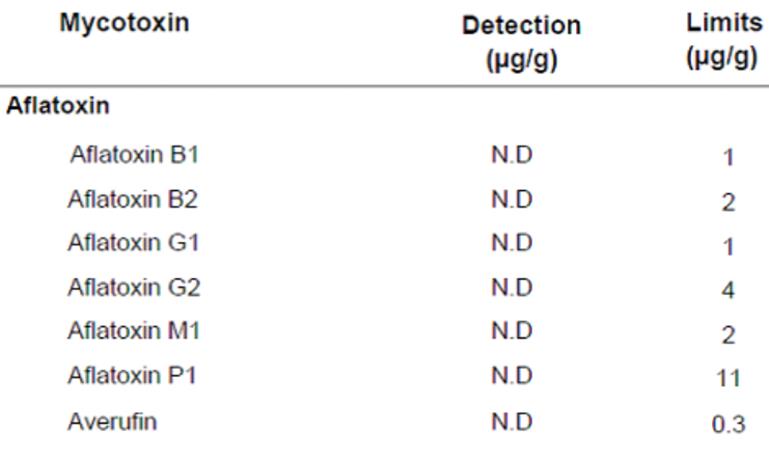
This lab analysis typically shows N.D. which a Not Detected
In the right-hand column of the following excerpt, the lab analysis shows the detection sensitivity. Detection limits are in parts per billion and this analysis of only 1 microgram per gram of surface dust. The issue is unless you have so much contamination you are unlikely to identify it.
Not only do you have to identify the mycotoxin but the area of deposition too. While it is accepted that mycotoxins can cause serious health issues, it is also accepted that other more readily identified markers of equal or even greater significance can be identified easier.
More importantly most mycotoxin tests only accommodate food-based spoilage mycotoxins.
You can utilise labs that search for many other mycotoxins but you may or may not find them in blood or urine results
If you have one pathogen your almost certain to have other species and mycotoxins as bad as they might be, only make up a small percentage of risk and health impact.
Professional Indoor Environmental Health experts can guide you on sampling and analysis and qualify surface decontamination protocols to include mycotoxins.
Remember if you have toxigenic mould and chemical inflammagens, you are likely to have mycotoxins too. The removal and or risk reduction of one should also be beneficial in decontamination of other issues. You can get more information from

01.
01.
WORLD-CLASS TECHNOLOGY
02.
02.
QUALITY STANDART
03.
03.
PRODUCTIVE CAPACITY
Fill the Form or
CALL US

02034320213
Don’t hesitate to contact us
info@mycotoxins.uk
Don’t hesitate to contact us
Working Time
Mon-Fri: 9:00 - 18:00 / Closed on weekends
